Pointing a satellite “dish” at a satellite is a simple process, but it requires a person to have at least basic skills in working with antenna equipment. In most cases, it is recommended to entrust the procedure to an experienced specialist, but if for any reason (secure object, remote location, etc.) it is not possible to use his services, then you can try to
adjust the antenna yourself .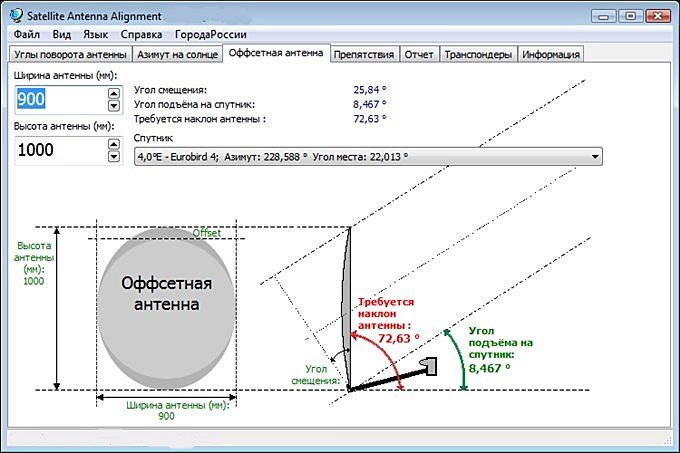
How to set the elevation angle on the satellite dish and the azimuth to the satellite
Before proceeding with direct guidance to the satellite, it is necessary to find out and record the values of the required parameters.
- Antenna location coordinates . You can find out the coordinates in one of several ways – using a GPS navigator, using applications such as GoogleMaps and the like, using a geographical map or in another available way. If you have a smartphone and are in the coverage area of the cellular network, determining the coordinates should not be difficult.
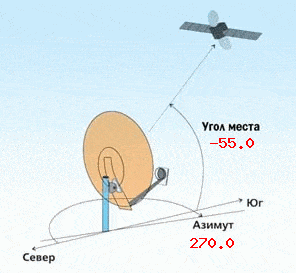
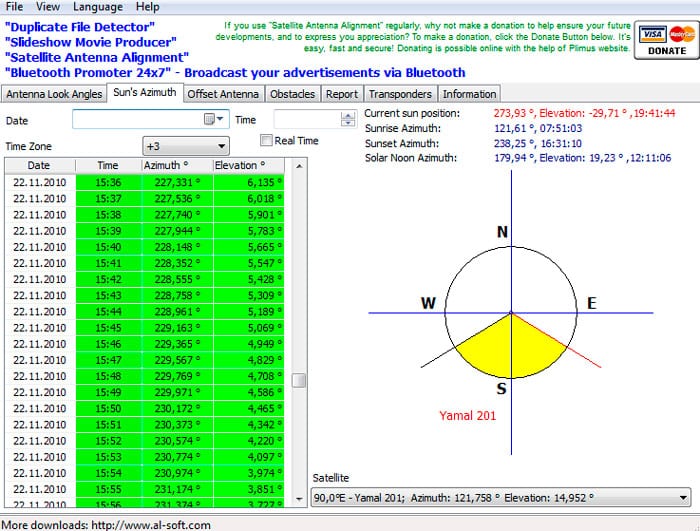
- Elevation and azimuth to the satellite . The most crucial moment in the entire process of tuning the antenna. If these data are not reliably known initially, then to determine them, it is recommended to use one of the Internet services, for example, the free online calculator “Satcalc”.
An azimuth and elevation calculator for self-tuning a satellite dish can be found at https://www.satcalc.ru/angle.php?s=&s_min=&s_sec=&d=&d_min=&d_sec=&d_0=140e&n_0=140e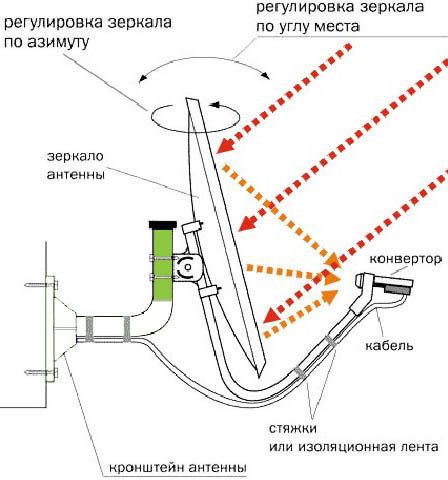
An example of calculating the direction to the satellite using a calculator
Consider the process of determining the direction of the antenna pointing using the example of the Express AM3 satellite in the city of Vladivostok. We determine the coordinates of the antenna installation point by any of the available methods. For the city of Vladivostok, the coordinates will have the following values - latitude: 43°06′20″, longitude: 131°52′24″ E. Go to the online calculator page.
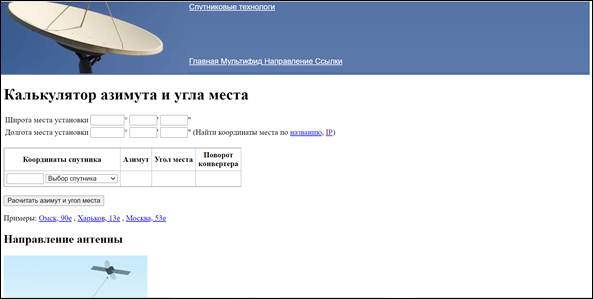 One of the advantages of this online calculator is the function of automatically determining the coordinates by the name of the settlement, according to the geolocation of the smartphone or by the IP address of the device (phone, laptop, PC) from which the site was accessed. Enter coordinates.
One of the advantages of this online calculator is the function of automatically determining the coordinates by the name of the settlement, according to the geolocation of the smartphone or by the IP address of the device (phone, laptop, PC) from which the site was accessed. Enter coordinates.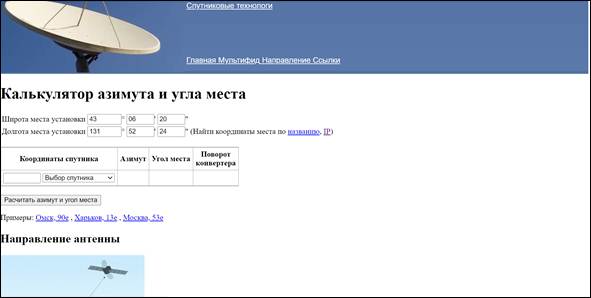 In a special window, select the satellite to which guidance will be carried out, in our case Express AM3.
In a special window, select the satellite to which guidance will be carried out, in our case Express AM3.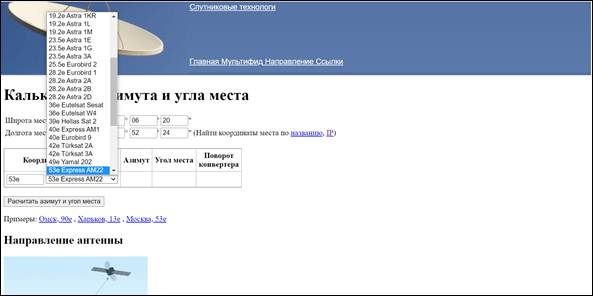 Click on the pop-up button “Calculate Azimuth and Elevation”.
Click on the pop-up button “Calculate Azimuth and Elevation”.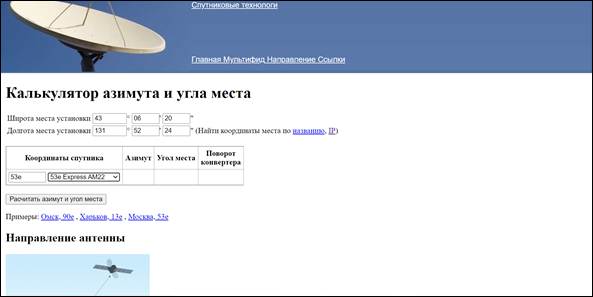 We get the required data.
We get the required data.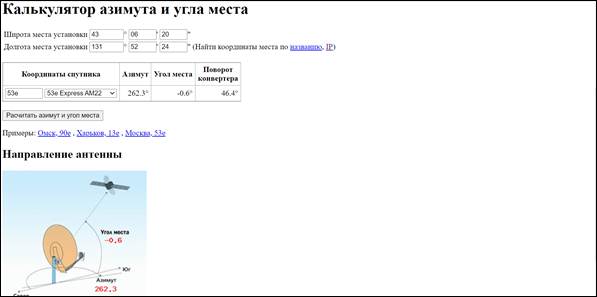 There is one more parameter in the information field – “Converter rotation”, this is an important parameter, more about it will be described in the antenna mounting section.
There is one more parameter in the information field – “Converter rotation”, this is an important parameter, more about it will be described in the antenna mounting section.
Selecting an installation point
When installing an antenna, you should focus on three main factors.
- The most open place in the direction of the satellite , ideally a direct line of sight, not blocked by buildings, trees, landscape hills.
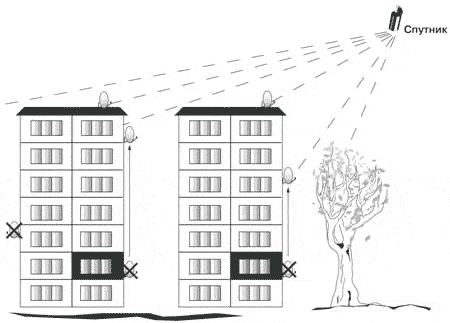
Choosing the right place to install a satellite dish is the first task - Reliability of antenna mounting . As a rule, the mirror of a satellite dish, due to design features, has an increased windage and, if not securely fastened, will oscillate from the wind.

- Keep the distance from the antenna to the satellite receiver as short as possible . The fact is that any cable introduces its own attenuation coefficient – that is, it lowers the level of the useful signal. In this regard, even when using a high-quality cable, it is not recommended to move the antenna away from the receiver by more than 20-25 meters.
The selected mounting location should also provide the ability to rotate the antenna mirror by 10-14 degrees from the azimuth axis. If there is a natural (artificial) obstacle in the direction of the satellite at a small distance, you can try to determine the degree of its possible influence on the reception quality.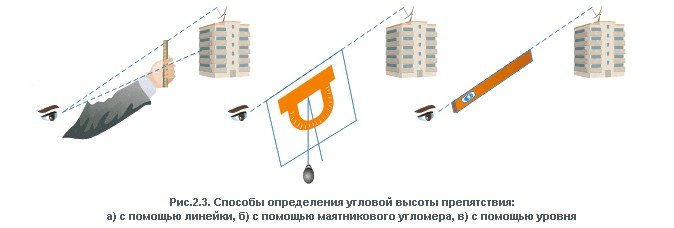 For the calculation, it is necessary to approximately determine the distance to the object and its height (for example, by comparing the height of nearby objects with the height of which is known), then using a trigonometric calculation or any of the Internet services, calculate the angle of elevation to the object. If the obtained value does not exceed the value of the elevation (elevation) angle, then there is nothing to worry about, otherwise you need to choose another place to install the antenna or use a support to increase the height.
For the calculation, it is necessary to approximately determine the distance to the object and its height (for example, by comparing the height of nearby objects with the height of which is known), then using a trigonometric calculation or any of the Internet services, calculate the angle of elevation to the object. If the obtained value does not exceed the value of the elevation (elevation) angle, then there is nothing to worry about, otherwise you need to choose another place to install the antenna or use a support to increase the height.
Determining the coordinates of your location for installing a satellite dish – these data are needed to calculate the azimuth and elevation angle of the satellite dish using a calculator or special software:
https://youtu.be/ST37xcEFxpY
Installation of antenna equipment
The process of mounting the antenna begins with its assembly. When assembling, you need to focus on the manufacturer’s recommendations. As a rule, the antenna comes with detailed instructions for assembling it, indicating the main parameters.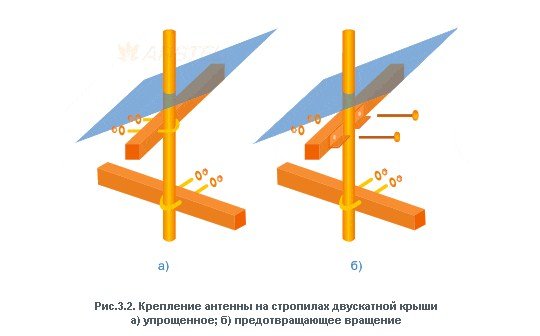
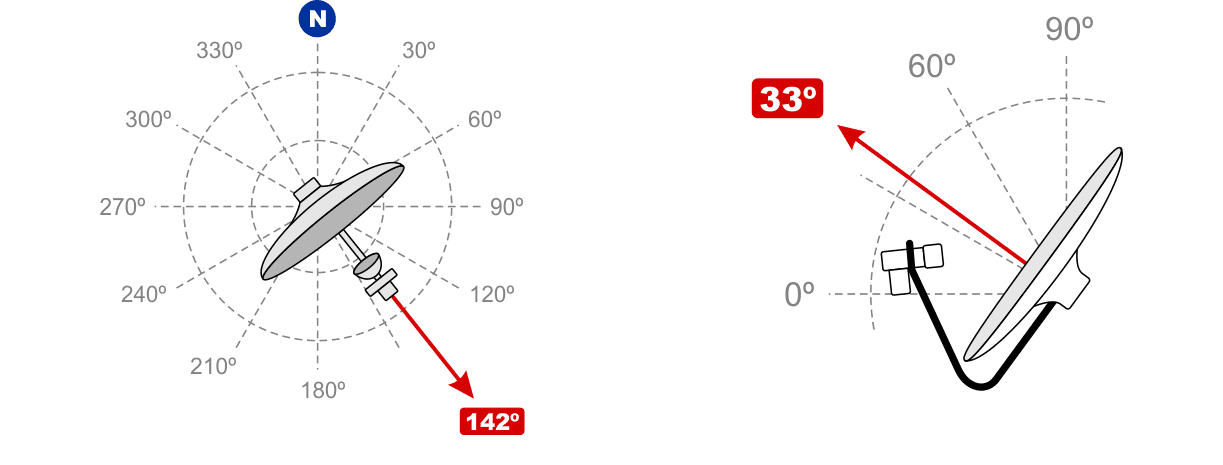
. The converter is mounted at the focus of the fully assembled antenna and rotated to the angle value obtained in the Satcalc program at the stage of calculating the azimuth and elevation angle. The value in the LNB Rotation column indicates that the LNB needs to be rotated 46 degrees counterclockwise from the vertical. For the convenience of setting the angle, markings are applied on the front of the converter indicating the “Zero position” and the angular scale. The final step in mounting the antenna is to connect the cable to the labeled converter.
Antenna tuning
Satellite dishes are divided into “Direct Focus” and “Offset”. You can distinguish them both by reading the attached documentation, and visually – direct-focus ones have a round configuration, the mirror of offset antennas has the shape of an ellipse (more elongated in the direction of the vertical axes). Each of the antennas has its own pointing features – the plane of the mirror of a direct-focus antenna is directed to the satellite during tuning in accordance with the elevation data. The offset antenna has an additional parameter – “offset angle”, its value can be found in the documentation for the antenna.
When setting up an offset antenna, the required position of the mirror plane is calculated by the formula – ƛp = ƛm – ƛs. Where ƛp is the required position of the offset antenna mirror relative to the horizontal, ƛm is the elevation angle calculated by the software method, ƛs is the offset angle specified in the antenna passport. It happens that after the calculation, the value is obtained with a minus sign, which means that the offset antenna mirror must be tilted down by the value of the obtained angle.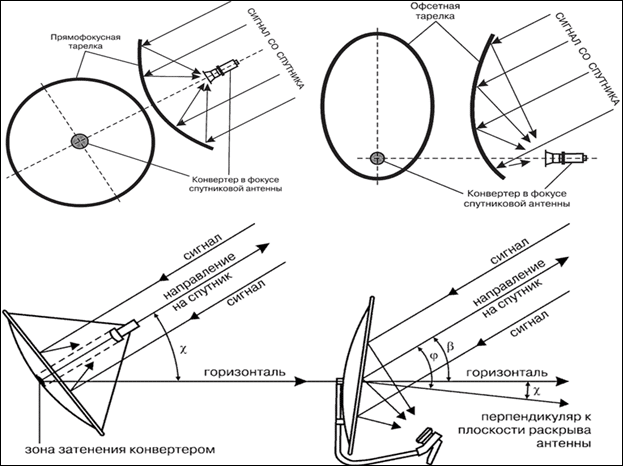 The azimuth and elevation angle of a satellite dish can be calculated without a calculator – through the formulas:
The azimuth and elevation angle of a satellite dish can be calculated without a calculator – through the formulas: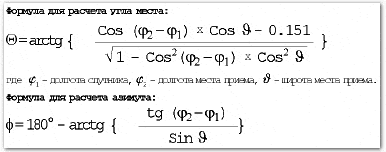
“Search” satellite
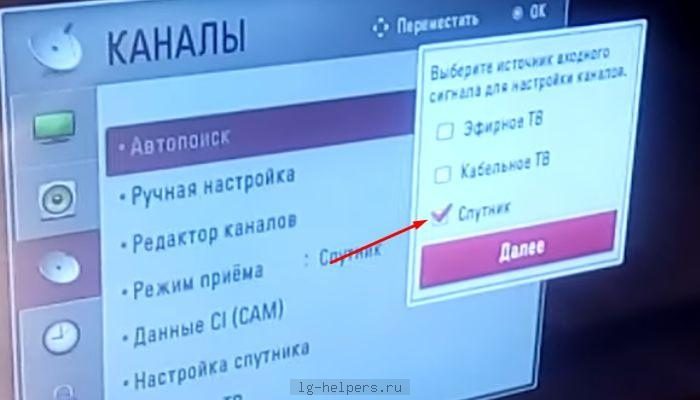
The direct pointing of the antenna to the satellite can be divided into two stages. At the first stage, a “rough” adjustment is made, at the second it is already final. Coarse tuning refers to pointing the antenna at the satellite in azimuth and elevation. To do this, the antenna mirror is raised by the calculated elevation angle (taking into account the offset angle of the antenna itself). At this stage, a goniometer attached to the antenna plane will come in handy.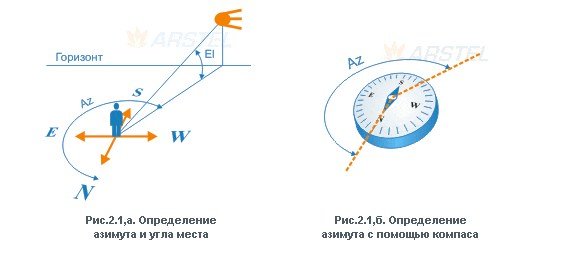 Azimuth guidance is performed using a compass. There is also a pointing method “according to the sun”, it gives good results, but in practice few people use it due to its limited application (cloudiness, it is not always possible to calculate the exact position of the sun at the right time, etc.). The final adjustment is made by including a special meter – “SatFinder” in the cable gap between the converter and the satellite receiver. Meters can be simple dial and more complex digital. In any case, any of them perform their functionality.
Azimuth guidance is performed using a compass. There is also a pointing method “according to the sun”, it gives good results, but in practice few people use it due to its limited application (cloudiness, it is not always possible to calculate the exact position of the sun at the right time, etc.). The final adjustment is made by including a special meter – “SatFinder” in the cable gap between the converter and the satellite receiver. Meters can be simple dial and more complex digital. In any case, any of them perform their functionality. For fine tuning, loosen the antenna bolts and slowly rotate it in azimuth, trying not to exceed a rotation speed of 1 degree per second. After capturing the signal, the methods of small turns (left/right) need to achieve the maximum signal level and fix the antenna. If a signal appears, but practically does not react to mirror turns or the quality is unstable, it is recommended to deflect the antenna by 1-2 degrees along the vertical axis relative to the elevation angle. The best results in the shortest possible time can be achieved using a spectrum analyzer as a meter, but this device is quite expensive and its purchase for the sake of one or two rare cases of antenna tuning is impractical. If absolutely necessary, you can set up a satellite dish without any devices at all. To do this, a satellite receiver and a TV (a laptop with a TV module) are placed near the dish itself, and the received signal is monitored on the scale of the receiver’s own setup program. At the same time, of course, it is not possible to achieve the highest possible quality, but this method is quite suitable for home use.
For fine tuning, loosen the antenna bolts and slowly rotate it in azimuth, trying not to exceed a rotation speed of 1 degree per second. After capturing the signal, the methods of small turns (left/right) need to achieve the maximum signal level and fix the antenna. If a signal appears, but practically does not react to mirror turns or the quality is unstable, it is recommended to deflect the antenna by 1-2 degrees along the vertical axis relative to the elevation angle. The best results in the shortest possible time can be achieved using a spectrum analyzer as a meter, but this device is quite expensive and its purchase for the sake of one or two rare cases of antenna tuning is impractical. If absolutely necessary, you can set up a satellite dish without any devices at all. To do this, a satellite receiver and a TV (a laptop with a TV module) are placed near the dish itself, and the received signal is monitored on the scale of the receiver’s own setup program. At the same time, of course, it is not possible to achieve the highest possible quality, but this method is quite suitable for home use.